Abu Dhabi hides layers of history beneath its modern skyline. Ancient tombs, forgotten settlements, and old fortresses reveal stories of early civilizations. Exploring these sites offers more than a glimpse into the past—it connects visitors to traditions that shaped the region. Best things to do to discover Abu Dhabi’s ancient history include visiting archaeological parks, desert tombs, and well-preserved oases. Each location uncovers a different piece of the puzzle, blending history, culture, and architectural ingenuity.
QASR AL HOSN: THE SENTINEL OF ABU DHABI’S HERITAGE
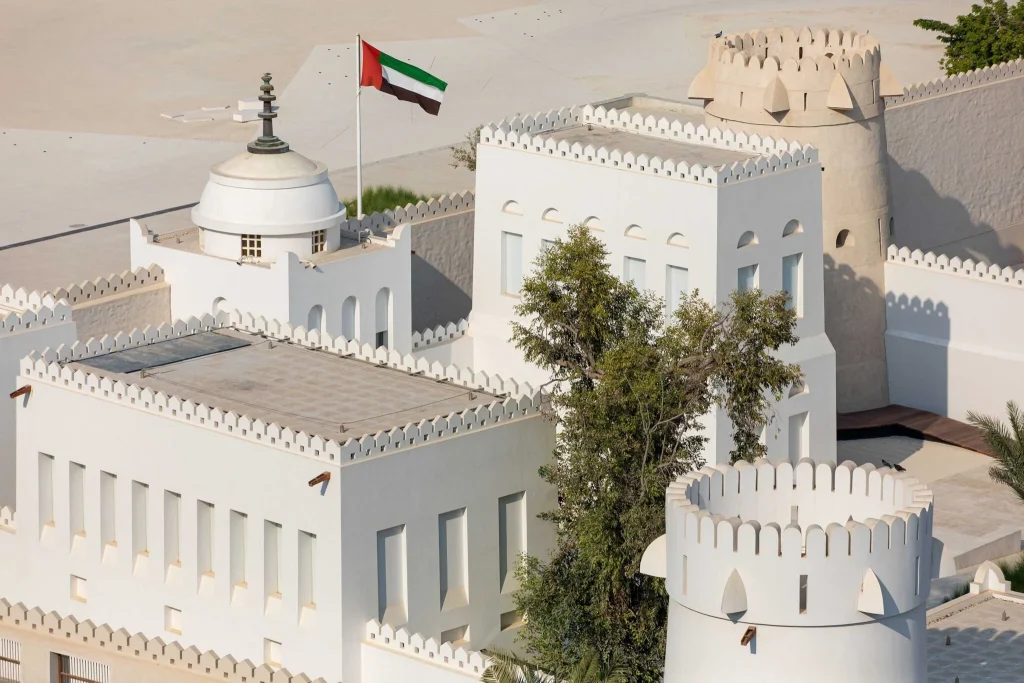
In the heart of Abu Dhabi stands Qasr Al Hosn, the city’s oldest stone building. Originally, constructed in the 18th century as a watchtower, it safeguarded precious water sources. Over time, it evolved into a fortified palace, serving as the residence of the ruling Al Nahyan family. The fort witnessed key events, such as treaties and the discovery of oil. Its architecture reflects a blend of Emirati design and defensive features.
Today, Qasr Al Hosn functions as a museum, narrating Abu Dhabi’s journey from a pearling village to a modern metropolis. Exhibits include artifacts, photographs, and oral histories. The site’s recent restoration preserved original materials, maintaining its historical integrity. Visitors can explore the Inner Fort, Outer Palace, and the House of Artisans. Qasr Al Hosn stands as a symbol of resilience and cultural identity.

HILI ARCHAEOLOGICAL PARK
In the heart of Al Ain, Hili Archaeological Park stands as a testament to ancient civilizations. This site showcases remnants from the Bronze Age, notably the Hili Grand Tomb, a circular structure spanning 12 meters in diameter. Adjacent to the tomb, excavations have unveiled settlements and irrigation systems, shedding light on early agrarian practices. Artifacts such as pottery and tools unearthed here indicate a society engaged in regional trade and craftsmanship.
The park’s layout, interspersed with lush greenery, offers visitors a serene environment to reflect upon the ingenuity of early inhabitants. Interpretive signage throughout provides insights into the site’s historical significance, though some details remain subjects of ongoing research. Notably, the discovery of 3,000-year-old fingerprints at Hili II offers a tangible connection to the artisans of yesteryears. While the park is a focal point, the surrounding Al Ain region is replete with archaeological wonders awaiting exploration. Visitors are encouraged to delve deeper into these sites to fully appreciate the rich tapestry of Abu Dhabi’s ancient history.

ANCIENT MARAWAH ISLAND: UNEARTHING MILLENNIA-OLD SECRETS
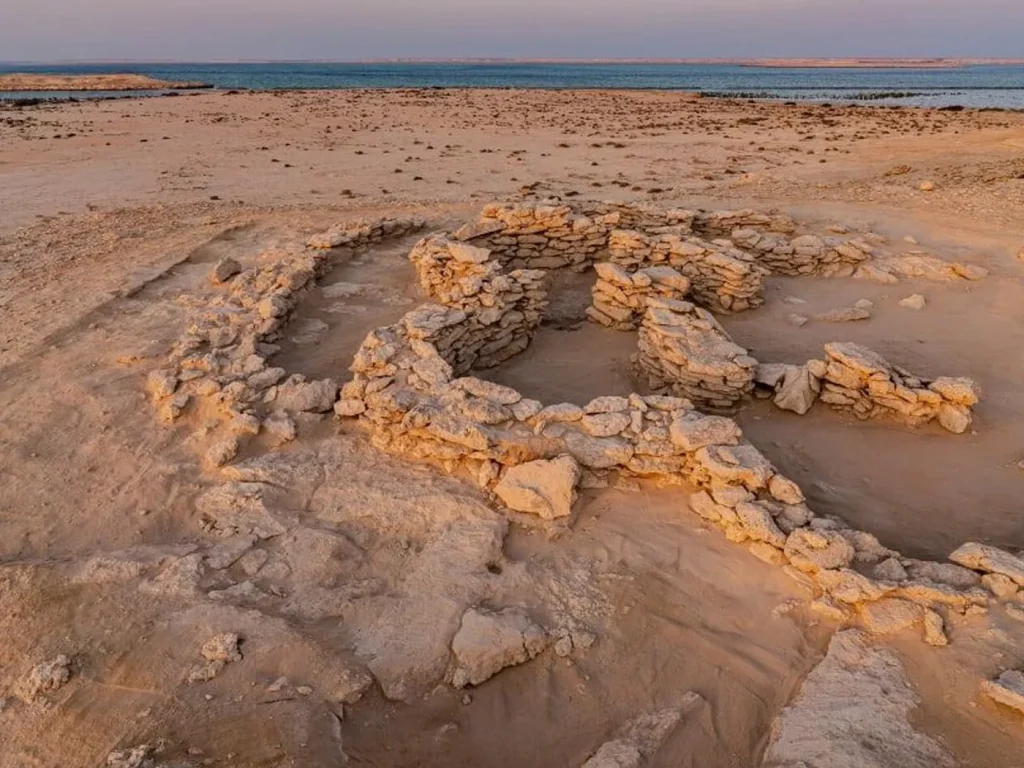
Off Abu Dhabi’s coast lies Marawah Island, a treasure trove of archaeological wonders. Excavations have revealed artifacts dating back over 7,000 years, including one of the world’s oldest natural pearls. These findings shed light on the island’s significance in early human settlement and maritime trade. The discovery of a 7,500-year-old skeleton offers a rare glimpse into Neolithic burial practices. Additionally, remnants of ancient structures suggest a sophisticated community engaged in fishing and pearl diving.
The island’s strategic location made it a hub for cultural exchanges across the Arabian Gulf. Today, Marawah stands as a testament to Abu Dhabi’s rich prehistoric heritage. Its ongoing archaeological projects continue to unveil secrets of the past. Visitors and scholars alike are drawn to its historical and cultural significance. Marawah Island remains pivotal in understanding the region’s ancient civilizations.

QATTARA OASIS: A LIVING LEGACY OF ANCIENT INGENUITY
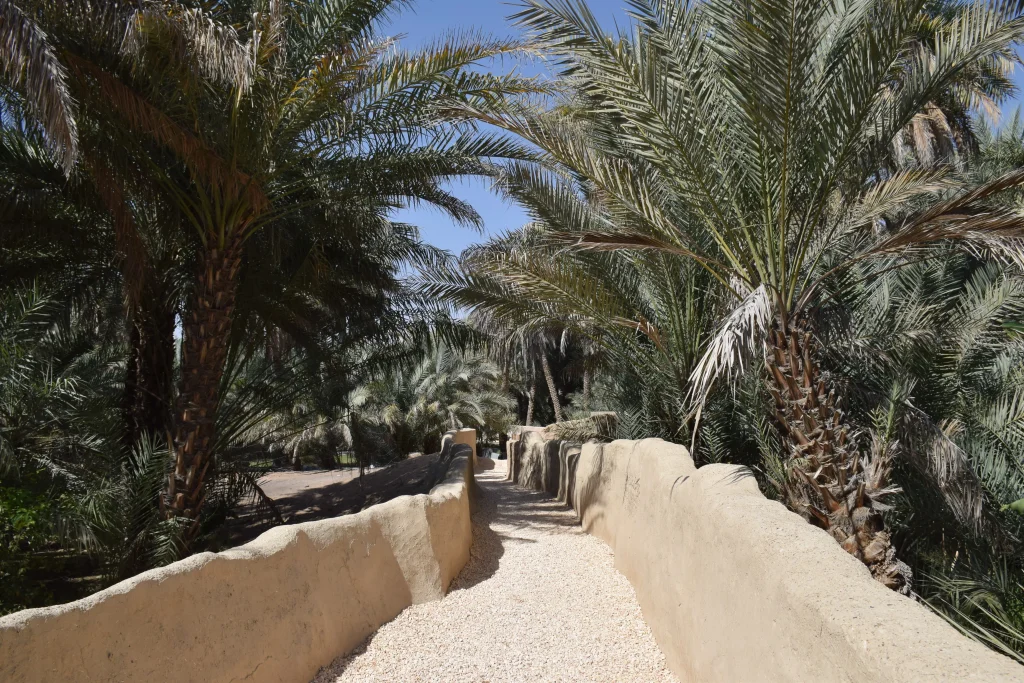
Nestled in Al Ain, Qattara Oasis exemplifies the ingenuity of early Emirati communities. The oasis thrives due to the ancient falaj irrigation system, channeling water from distant sources. Archaeological evidence indicates human habitation dating back to the Bronze Age. Artifacts such as pottery and tools reveal a community adept in agriculture and trade. The oasis also features traditional mud-brick structures, reflecting vernacular architecture.
Its souq, established in the 1930s, remains a bustling center of commerce. The Al Daramikah Tower stands sentinel, protecting the oasis and its resources. Qattara’s cultural significance is further highlighted by its art center, promoting local crafts. The oasis embodies a harmonious blend of nature, history, and community. Exploring Qattara offers insights into sustainable practices of ancient civilizations.

BIDAA BINT SAUD: CHRONICLES OF EARLY INNOVATIONS
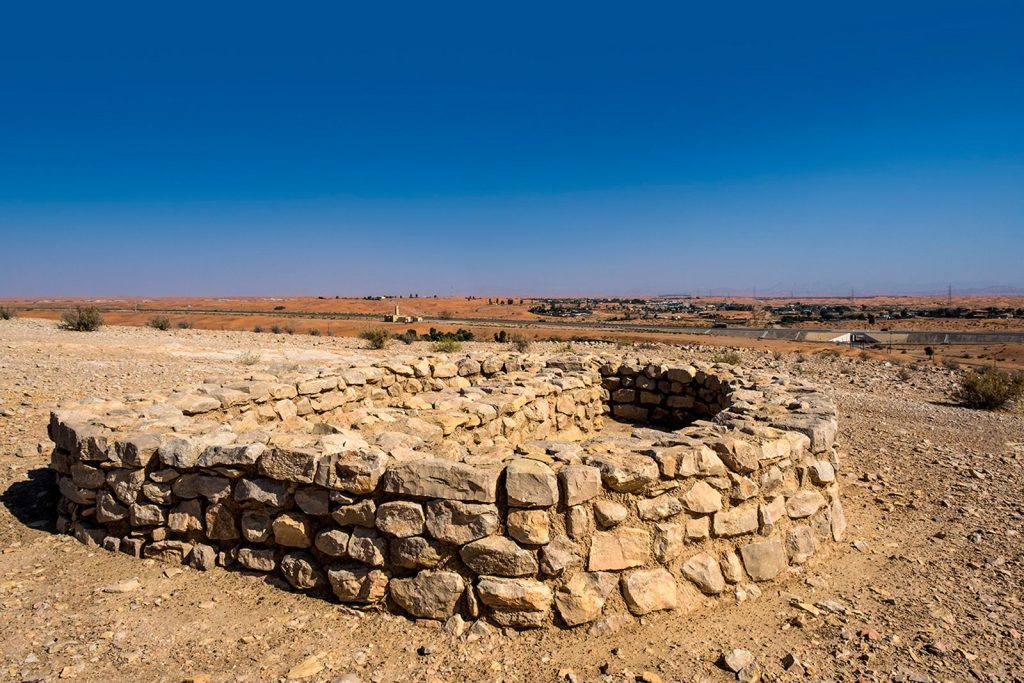
Bidaa Bint Saud, located north of Al Ain, is an archaeological site of profound importance. The area is renowned for its Hafit-period beehive tombs, dating back over 5,000 years. These tombs provide insights into early burial customs and social structures. Significantly, the site contains one of the oldest known falaj systems, an ancient irrigation method. This innovation highlights the community’s advanced agricultural practices during the Iron Age.
Remnants of a mud-brick building suggest a center for water distribution and administration. Artifacts such as pottery and bronze tools indicate a society engaged in trade and craftsmanship. The site’s strategic location implies its role as a caravan stop between regions. Bidaa Bint Saud enriches our understanding of technological advancements in early Arabia. Ongoing research continues to unveil the site’s historical significance.

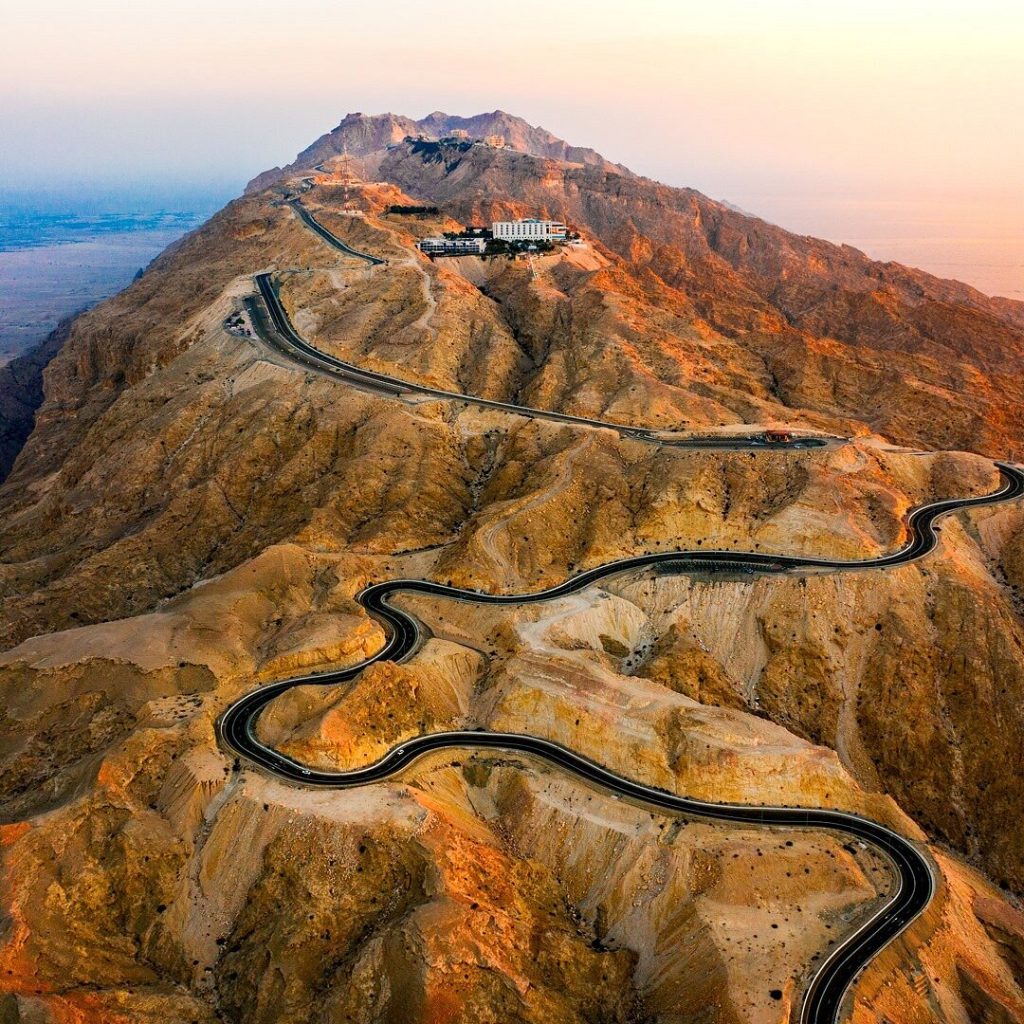
JEBEL HAFIT DESERT PARK: A JOURNEY THROUGH TIME
Jebel Hafit Desert Park, located in Al Ain, offers a unique blend of natural beauty and archaeological significance. The park encompasses Jebel Hafit, Abu Dhabi’s highest peak, and its surrounding landscape. Over 500 beehive tombs, dating to the Hafit period, dot the foothills, marking early burial practices. These tombs have yielded artifacts indicating trade links with Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley. The park’s diverse ecosystems support a variety of flora and fauna, including rare species.
Visitors can engage in activities such as hiking, mountain biking, and guided archaeological tours. The park also offers overnight camping experiences, allowing for stargazing in a pristine environment. Educational programs provide insights into the region’s geology, ecology, and history. Jebel Hafit Desert Park stands as a bridge between Abu Dhabi’s ancient past and its natural wonders.



 then "Add to Home Screen"
then "Add to Home Screen"